Today, I want to tell you about of gambling in Nevada, great state, perhaps the most powerful and iconic brand in the global gambling industry. Las Vegas. “What happens in Vegas, stays in Vegas.” That famous phrase alone evokes excitement. For people around the world, playing in Vegas is a dream, something you do at least once in your life.
I have two personal stories connected to this city.
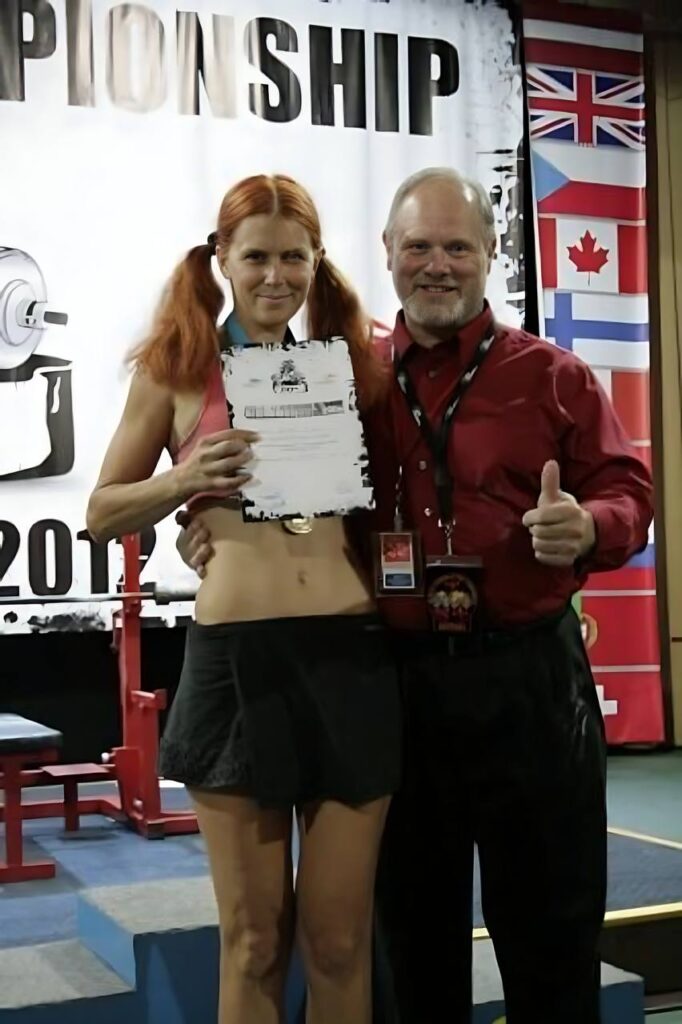
Fifteen years ago, my mother traveled to Las Vegas to compete in a weightlifting 2012 WPC Word Powerlifting Championships. She won. She earned the title of International Master of Sports. That night, she walked into a casino (Golden Nugget Casino) and placed a $100 bet on number 10 at the roulette table. Why 10? Because her eldest son, me, was born on June 10. And she won. That story isn’t fiction, it’s part of my family history.
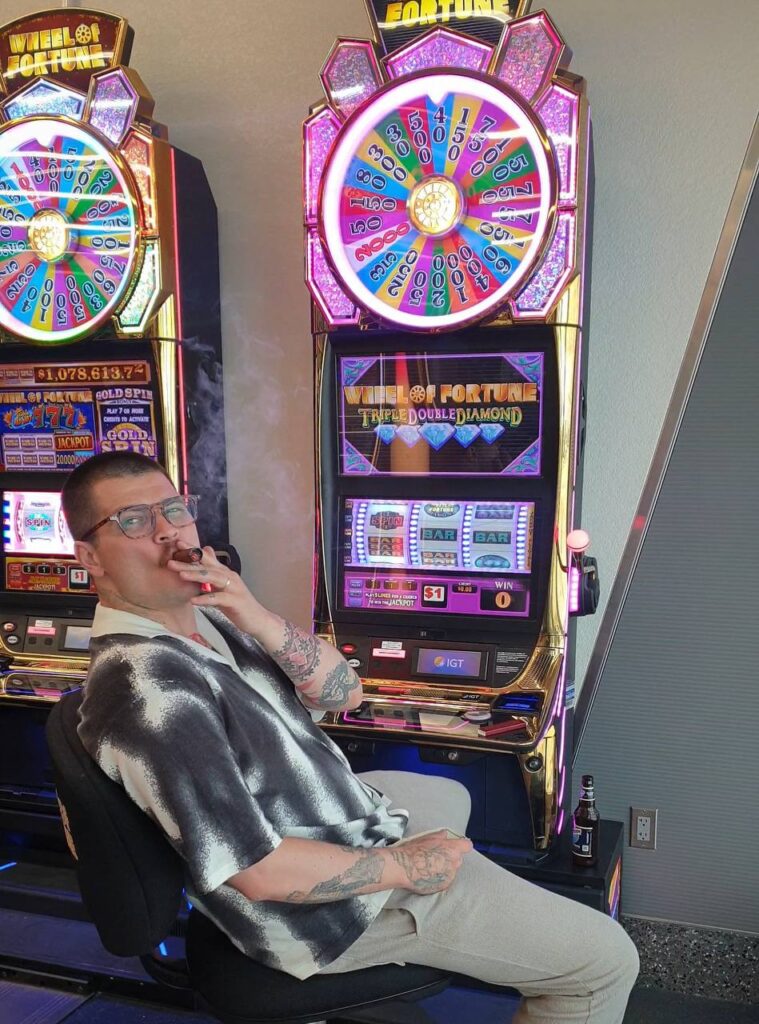
The second story wasn’t as lucky. Las Vegas was the first city my wife and I landed in when we arrived in the United States two years ago. We had a four-hour layover at the airport. There were slot machines right there. I gave her $50, kept $50 for myself, and we both lost. But the feeling of doing it, in that moment, together, was unforgettable.
I’ll include a photo from that memory. And we will definitely return to Vegas, not just once, but many times. I promise you that.
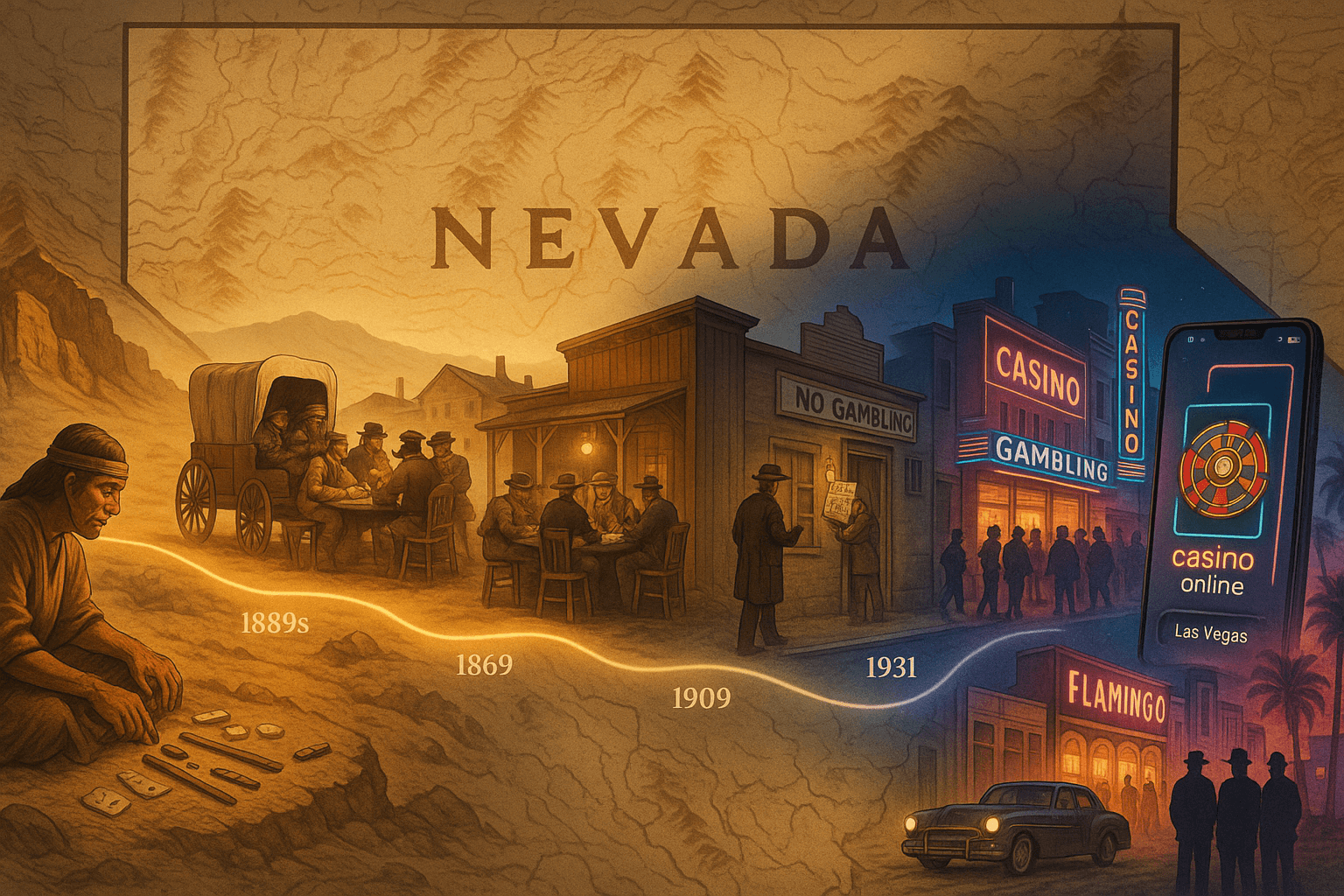
Early Encounters and Indigenous Games
Gambling in Nevada dates back long before the establishment of the state. Indigenous peoples living in the region, including the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes, practiced games of chance that involved wagering items such as beads, food, and ceremonial objects. These games were woven into cultural rituals and seasonal events (Nevada Historical Society Journal, Vol. 12, 1990, pp. 34–38).
With the arrival of European explorers and missionaries in the late 1700s and early 1800s, gambling practices began to evolve. These groups, including missionaries, fur trappers, and traders, brought with them European card games, dice games, and betting traditions. Notable among early explorers was Jedediah Smith, who traversed the region in the 1820s and interacted with local communities, including those engaged in gambling (Smith’s 1827 diary, p. 213 (Univ. of Utah)).
By the mid-1800s, gambling became commonplace in mining camps throughout the Nevada Territory. As the California Gold Rush expanded eastward, prospectors and miners settled in Nevada, establishing tent cities and permanent settlements. These frontier towns often included gambling halls, saloons, and backroom betting dens. Card games like faro, poker, and blackjack thrived alongside dice and roulette (UNLV Center for Gaming Research).


Development of Frontier Gambling in Nevada Culture (1861–1946)
In 1861, the Nevada Territory was formally established. Just three years later, in 1864, Nevada achieved statehood. Its early economy was heavily reliant on mining, particularly silver and gold. Gambling was widespread but largely unregulated, integrated into saloons, hotels, and brothels.
The 1869 legislative session legalized most forms of gambling, recognizing its popularity and revenue potential (Nevada Revised Statutes Historical Archive, Chapter 5 (1869)). This act established Nevada as one of the few places in post-Civil War America where gambling was openly permitted by law.
By the early 1900s, public sentiment shifted. National campaigns against vice and moral corruption led to new laws banning most gambling activities. In 1909, Nevada repealed its gambling legalization and made it illegal, except for limited social games (Nevada Session Laws 1909, Chapter 112).
Despite the ban, illegal gambling operations continued to thrive. Underground poker rooms, dice games, and betting houses operated with impunity in mining towns and larger cities such as Reno. This era was marked by corruption, with law enforcement often ignoring violations in exchange for payoffs.
In 1931, the Nevada state legislature re-legalized casino gambling in an attempt to combat economic collapse during the Great Depression. This marked a turning point in American gambling history. Las Vegas and Reno saw an explosion of casinos and gaming halls. The first casino to receive a license under the new law was the Northern Club in Las Vegas (Las Vegas Review-Journal archive, Sept 1931).
From 1931 to 1946, the state’s gambling industry expanded rapidly. Las Vegas grew from a railroad town into a hub for entertainment and vice. Meanwhile, Reno developed a reputation as a gaming and quick-divorce capital.
The Rise of Las Vegas and Regulation (1946–2018)
In 1946, Bugsy Siegel opened the Flamingo Hotel, ushering in a new era of luxury casinos (Las Vegas Review-Journal Dec 27, 1946). With mob financing, glitzy properties emerged, attracting tourists, celebrities, and political elites. The post-WWII boom brought highways, air travel, and suburban expansion all factors that fueled Vegas growth.
The 1950s and 60s saw federal scrutiny of organized crime in casinos. The Nevada Gaming Control Board was established in 1955 to oversee licensing and enforce integrity standards (Nevada Gaming Commission History). In 1959, the Nevada Gaming Commission was formed, adding further oversight and legal power.
Through the 1970s and 80s, corporate ownership began to replace mob control. Major brands such as Hilton, MGM, and Caesars entered the market. The development of themed resorts like Caesars Palace, The Mirage, and Excalibur drew global attention.
In 1995, the Martin Scorsese film “Casino” dramatized the rise and fall of mob influence in Las Vegas, based on real-life events involving the Tangiers (inspired by the Stardust) and key mob figures (IMDb – Casino Trivia). The film added global pop culture significance to Nevada’s gambling image.
By the 2000s, Las Vegas had fully transitioned into a mainstream entertainment capital. The casino online Las Vegas market emerged alongside land-based venues. Hotels integrated with casinos began offering upscale amenities, shows, spas, and restaurants contributing to what is now a highly competitive Nevada hotel casino amenities guide for travelers.
Modern Trends and Taxation (2018–2025)
From 2018 to 2025, Nevada’s gambling landscape diversified. Sports betting was legalized across the U.S, allowing individual states to legalize and regulate sportsbooks on their own terms. in 2018 following the Supreme Court’s repeal of PASPA (SCOTUS slip opinion 17‑961). Though Nevada had offered legal sports wagering for decades, competition intensified nationwide.
Online casino platforms in Las Vegas gained popularity, though full-scale iGaming remains limited compared to states like New Jersey. However, mobile sports betting apps exploded in usage.
The History of Legal Gambling in New Jersey – read
In recent years, regulatory updates shaped operations across the state. The Nevada slot machine regulation update in 2023 introduced new auditing procedures, payout reporting, and digital compliance standards (Regulation R081‑22).
Simultaneously, policy discussions around Nevada casino tax rates news reflected the growing push for modernization and competitive tax strategies to retain operators and encourage innovation (Gaming Tax Report 2024).
Reno, often overshadowed by Las Vegas, announced a major expansion in 2025 with a new casino opening in Reno 2025 featuring luxury suites, live shows, and integrated sportsbook facilities (Reno Gazette-Journal Feb 2025). The project is expected to revitalize northern Nevada’s gaming industry.